2025-09-15 09:36 Tags: Bordeaux
what is statistic inference?
Statistical inference is the process of using sample data to make educated conclusions about a larger population, while carefully accounting for uncertainty.
 “
“
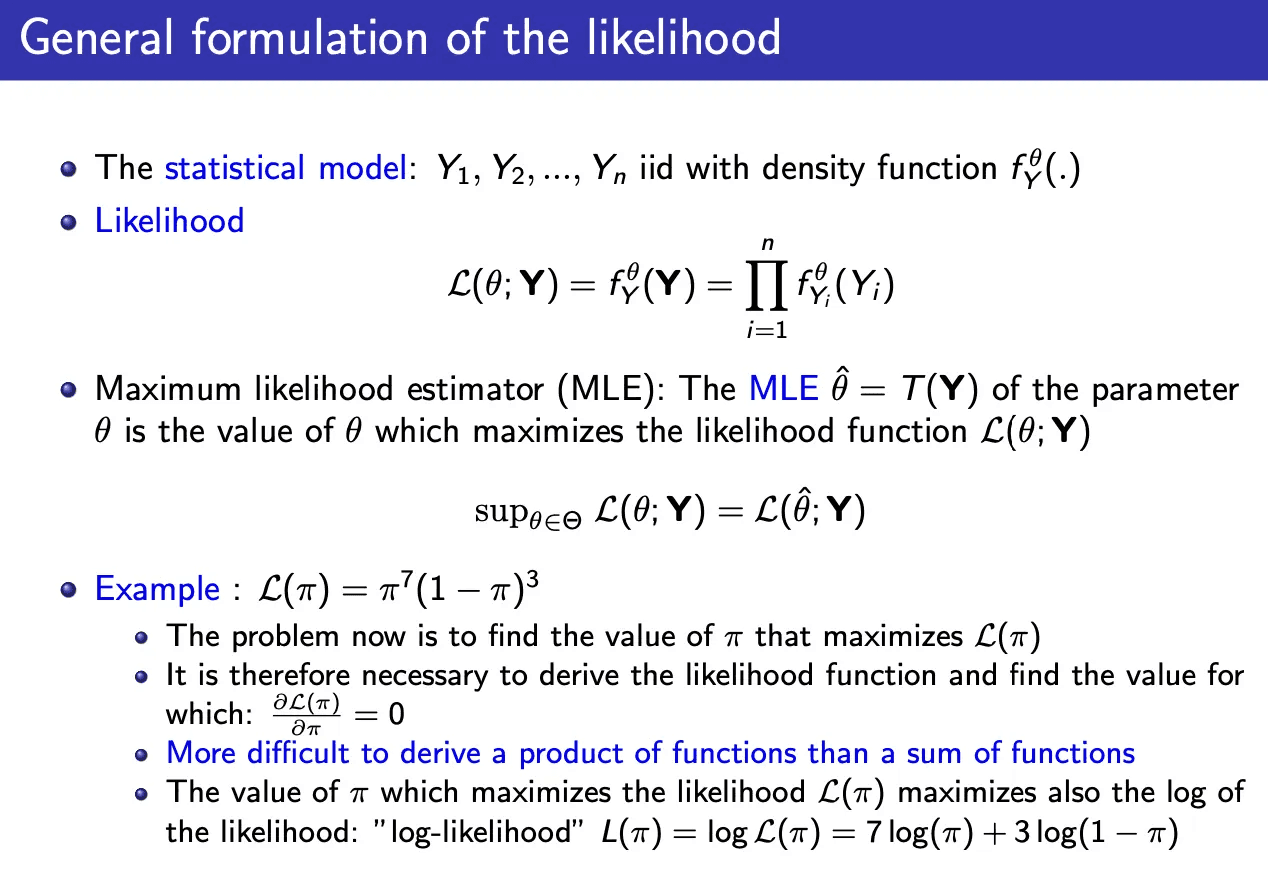
General formulation of the likelihood
1. Statistical model
We have data:
The statistical model assumes each observation comes from the same distribution depending on an unknown parameter (\theta).
2. Likelihood
The likelihood function is:
- Here the data (Y_i) are considered fixed once observed.
- The likelihood is a function of the parameter (\theta).
3. Maximum Likelihood Estimator (MLE)
The MLE is the value of (\theta) that maximizes the likelihood:
Equivalently:
4. Example: Bernoulli/Binomial case
Suppose we observed (7) successes and (3) failures.
The likelihood function is:
5. Log-likelihood
It is easier to maximize the log of the likelihood:
6. Derivation of the MLE
Differentiate the log-likelihood and set derivative to zero:
Solve for (\pi):
Thus, the MLE is:
✅ Key takeaways
- Likelihood = function of parameters given data.
- MLE = parameter value that maximizes likelihood.
- Log-likelihood simplifies products into sums.
- For Bernoulli/binomial models, the MLE is the sample proportion.