Official Guide and Documentation
Refer to the full pandas guide for more examples and advanced usage:
User Guide - Merging, Joining, and Concatenating
Concatenation
Concatenation allows you to “glue” DataFrames together either along rows (axis=0) or columns (axis=1).
Example DataFrames
import pandas as pd
data_one = {'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'], 'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']}
data_two = {'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3'], 'D': ['D0', 'D1', 'D2', 'D3']}
one = pd.DataFrame(data_one)
two = pd.DataFrame(data_two)Concatenate Along Rows (axis=0)
pd.concat([one, two], axis=0)
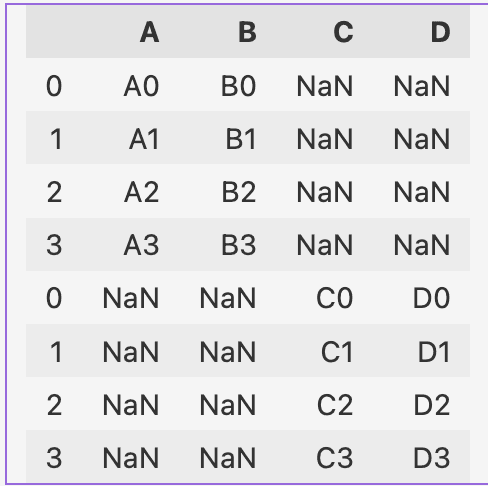
Concatenate Along Columns (axis=1)
pd.concat([one, two], axis=1)Matching Columns When Concatenating Rows
To ensure columns align when concatenating, rename the columns in two to match one:
two.columns = one.columns
pd.concat([one, two])Merging
Merging combines DataFrames based on key columns, similar to SQL joins. Use pd.merge() to perform a merge.
Example DataFrames
registrations = pd.DataFrame({'reg_id': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'name': ['Andrew', 'Bobo', 'Claire', 'David']})
logins = pd.DataFrame({'log_id': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'name': ['Xavier', 'Andrew', 'Yolanda', 'Bobo']})Inner Join
Match rows where the key exists in both DataFrames:
pd.merge(registrations, logins, how='inner', on='name')Left Join
Include all rows from the left DataFrame and match where possible. Fill unmatched rows with NaN:
pd.merge(registrations, logins, how='left')Right Join
Include all rows from the right DataFrame and match where possible. Fill unmatched rows with NaN:
pd.merge(registrations, logins, how='right')Outer Join
Include all rows from both DataFrames and fill unmatched rows with NaN:
pd.merge(registrations, logins, how='outer')Advanced Merging
Join on Index or Column
You can merge a column in one DataFrame with the index in another:
registrations = registrations.set_index("name")
pd.merge(registrations, logins, left_index=True, right_on="name")Joining Columns with Different Names
If key columns have different names, specify them explicitly using left_on and right_on:
registrations.columns = ['reg_name', 'reg_id']
pd.merge(registrations, logins, left_on='reg_name', right_on='name')Resolving Duplicate Column Names
Pandas automatically appends suffixes like _x (left) and _y (right) when columns overlap. You can set custom suffixes:
pd.merge(registrations, logins, on='name', suffixes=('_reg', '_log'))Summary
- Use
pd.concat()to stack DataFrames either vertically (axis=0) or horizontally (axis=1). - Use
pd.merge()for SQL-style joins:- Inner Join: Keep only matching rows.
- Left/Right Join: Keep all rows from one DataFrame, filling missing values with
NaN. - Outer Join: Combine all rows from both DataFrames, filling missing values with
NaN.
- Use advanced options like
left_on,right_on,suffixes, and index-based joins for greater control.